
Iron which is present in the middle of the table of the reactive series when reacted with sulfuric acid produces hydrogen and metal salt namely iron sulphate.į e ( s ) + H 2 S o 4 ( l ) → F e S o 4 ( a q ) + H 2 ( g ) It produces hydrogen and metal hydroxide when it reacts with cold water.Ģ N a ( S ) + 2 H 2 O ( l ) → 2 N a O H ( a q ) + H 2 ( g )
#METAL REACTIVITY TABLE FREE#
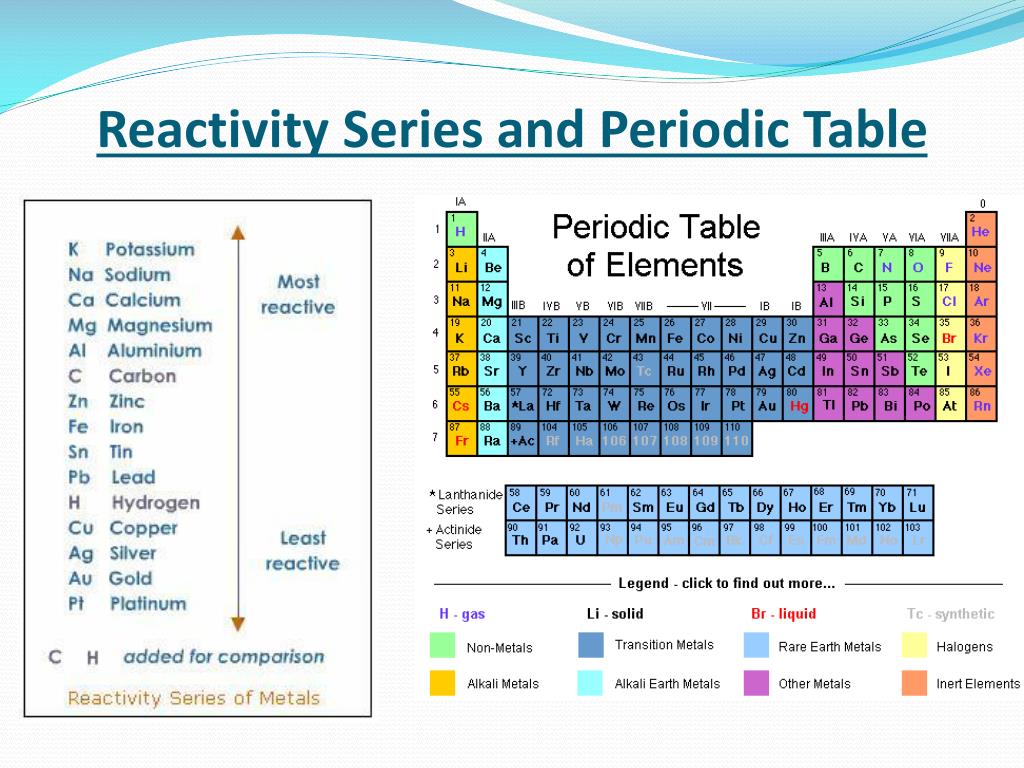
We can summarize the reactivity of metals in a reactivity series chart as shown below: Metalĭisplaces H 2 gas from water, steam and acids and forms hydroxides.ĭisplaces H 2 gas from steam and acids and forms hydroxides.ĭisplaces H 2 gas from acids only and forms hydroxides.Ĭombines with O 2 to form oxides and cannot displace H 2.įound free in nature, oxides decompose with heating. They require more energy to be separated from their ores, and become stronger reducing agents, while metals present at the bottom of the series are good oxidizing agent. Metals present at the top of the series can lose electrons more readily to form positive ions and corrode or tarnish more readily. In the reactivity series, as we move from bottom to top, the reactivity of metals increases.


Differences between metals & non-metals: S.NoĬan exist in solid, liquid & gaseous state It gives information regarding the reducing power of the metal atom and the oxidation number of the metal ion.īefore discussing the reactivity order of metals, it is important to discuss about the differences between metals and non-metals. The reactivity series of metals can be shown in another way, which includes oxidation reaction of each metal to the respective metal ion. In other words, all metals are good reducing agents and easily oxidize themselves. It gives a descriptive detail on metal reactions with the extraction of metals from ores and with acids and water. In other words, the most reactive metal is presented at the top and the least reactive metal at the bottom, as shown in the reactivity series chart below.Īll metals have a tendency to lose electrons and form metal ions. Reactivity Series in chemistry is an experimental, structural and logical progression of series of metals in order of reactivity from highest to lowest. Metals react differently with different substances.

Others, like palladium, platinum and gold do not react with the atmosphere at all. The transition metals (such as iron, copper, zinc, and nickel) are slower to oxidize because they form a passive layer of oxide that protects the interior. Examples: 4 Na + O 2 → 2 Na 2O (sodium oxide) 2 Ca + O 2 → 2 CaO (calcium oxide) 4 Al + 3 O 2 → 2 Al 2O 3 (aluminium oxide). Metals are usually inclined to form cations through electron loss, reacting with oxygen in the air to form oxides over various timescales (iron rusts over years, while potassium burns in seconds). This article is on reactivity series of metals. Typically they are malleable and ductile, deforming under stress without cleaving. In terms of optical properties, metals are shiny and lustrous. Metals, in general, are substances which have high electrical conductivity, high thermal conductivity, and high density.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
